Despite (or possibly because) multi-core systems development use the same programming languages, and largely similar design methods as single-core systems, migrating applications from single-core to multi-core systems can present some unexpected challenges.
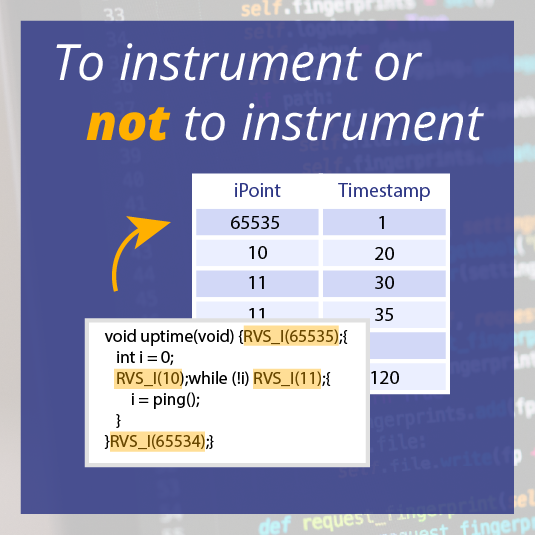
Recently I was experimenting with a multi-core system within the CRAFTERS project, running different code on each core. To see the application's timing, I had instrumented all of the code using RapiTime. The instrumentation is used to record which parts of the program are being run, and at what time. As a preliminary approach, the instrumentation code wrote into a memory buffer common to all cores.
This is the same approach I would take with a single-core, multitasking system. At the end of the test runs, the content of the buffer would be retrieved and demultiplexed to individual tasks (or cores in the case of multi-core systems). Timing measurements can then be attributed to individual tasks.
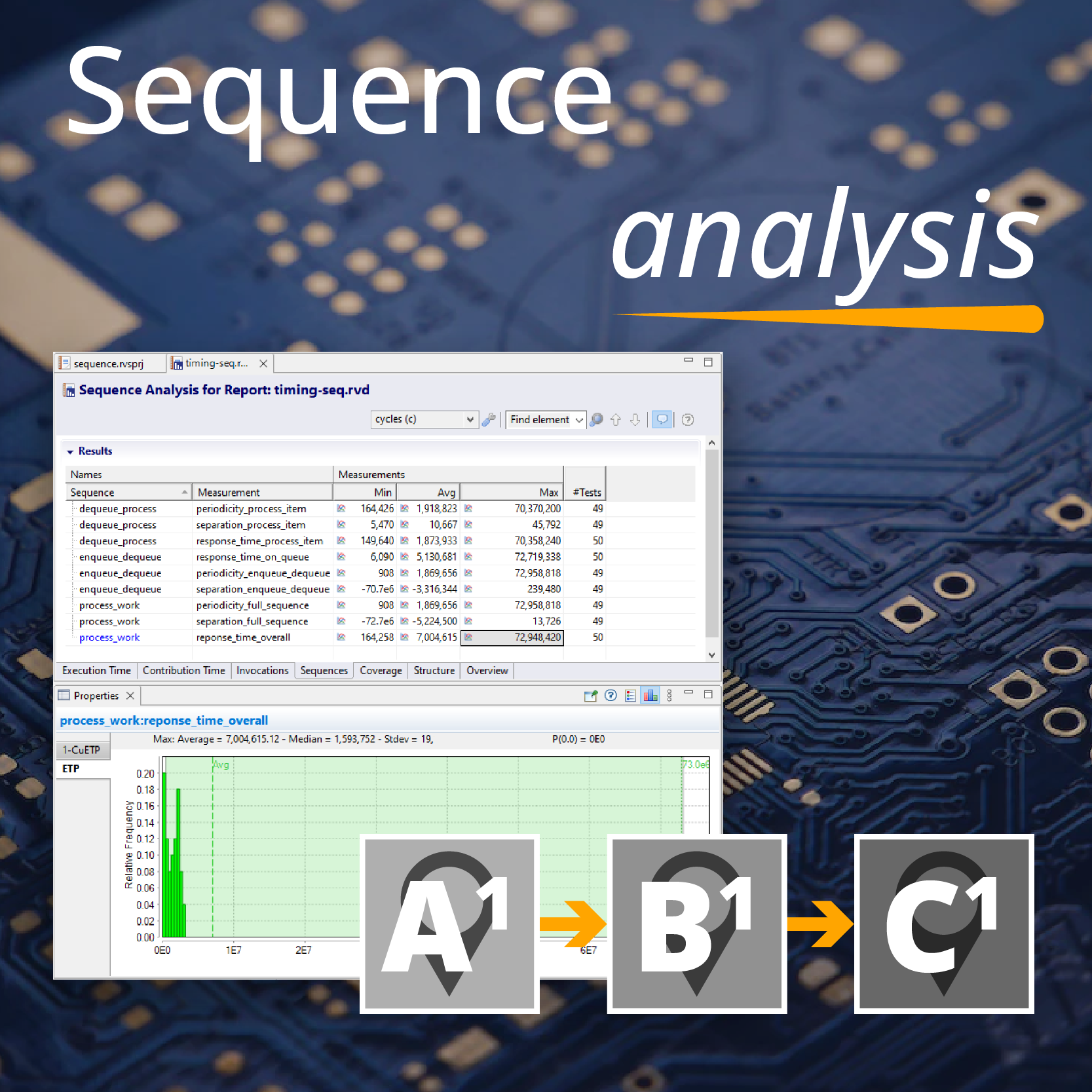
In the case of the multi-core system I was experimenting with, this approach led to some unexpected timing measurements, with a very high density of Ipoints. Investigating further, I noticed by inspecting the trace files that each of the cores executed almost exactly the same number of instrumentation points. This was peculiar because the code executing on each core was very different (see the RapiTask trace window screenshot) – I would have expected there to be a big difference between the number of instrumentation points executed, especially over a long test run.
The cause of this behavior turned out to be the bus arbitration for the processor. Writes to the shared memory take a (relatively) long time. Because the instrumentation code was executed relatively frequently, this led to frequent conflicts. As the bus arbitration was handled in a round-robin manner, the code was effectively being synchronized through the instrumentation points, leading to this unusual timing and Ipoint density the system experienced.
A simple resolution to this system was to modify the instrumentation to use local (per-core) memory, and avoid the involvement of the bus arbitration unit. This also had the benefit of making our instrumentation code faster.
This illustrates an important point about multi-core development: most of the issues that we are likely to experience arise from behaviors that are not directly related to the functionality of the code. Consequently, it is important to have access to tools such as RapiTask, which allow you to explore system behavior in detail, and to identify such anomalies, which is an essential precondition to being able to resolve them. 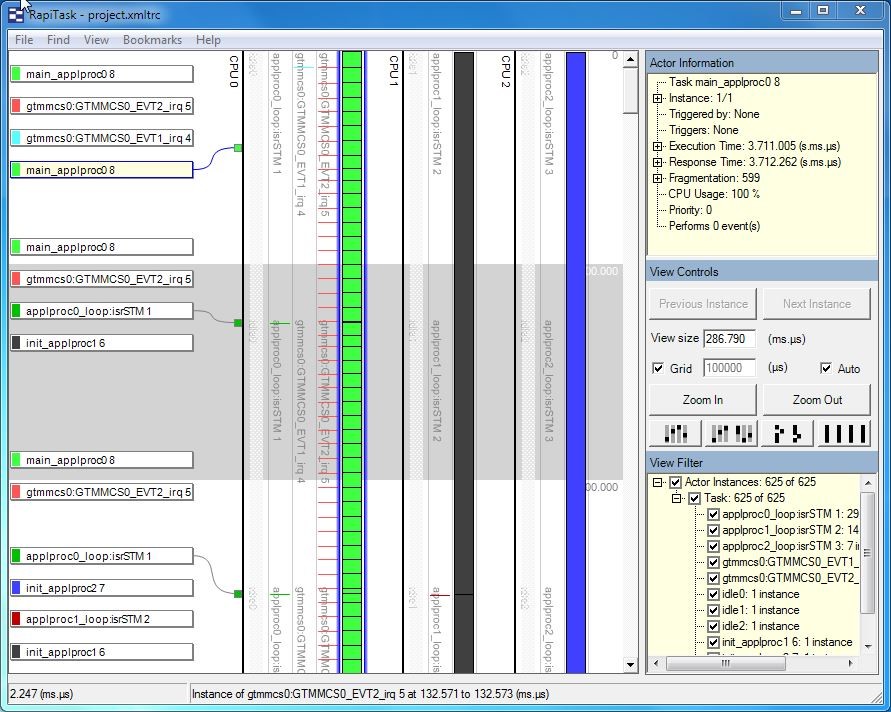

 RVS 3.24 accelerates multicore software verification
RVS 3.24 accelerates multicore software verification
 Rapita Systems and Avionyx Announce Strategic Partnership to Offer Best-in-class Avionics Solutions
Rapita Systems and Avionyx Announce Strategic Partnership to Offer Best-in-class Avionics Solutions
 Rapita System Announces New Distribution Partnership with COONTEC
Rapita System Announces New Distribution Partnership with COONTEC
 RVS gets a new timing analysis engine
RVS gets a new timing analysis engine
 How to measure stack usage through stack painting with RapiTest
How to measure stack usage through stack painting with RapiTest
 What does AMACC Rev B mean for multicore certification?
What does AMACC Rev B mean for multicore certification?
 How emulation can reduce avionics verification costs: Sim68020
How emulation can reduce avionics verification costs: Sim68020
 How to achieve multicore DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
How to achieve multicore DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
 How to achieve DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
How to achieve DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
 Certifying Unmanned Aircraft Systems
Certifying Unmanned Aircraft Systems
 DO-278A Guidance: Introduction to RTCA DO-278 approval
DO-278A Guidance: Introduction to RTCA DO-278 approval
 Embedded World 2026
Embedded World 2026
 Test what you fly - Real code, Real Conditions Webinar
Test what you fly - Real code, Real Conditions Webinar
 Avionics Certification Q&A: CERT TALK
Avionics Certification Q&A: CERT TALK