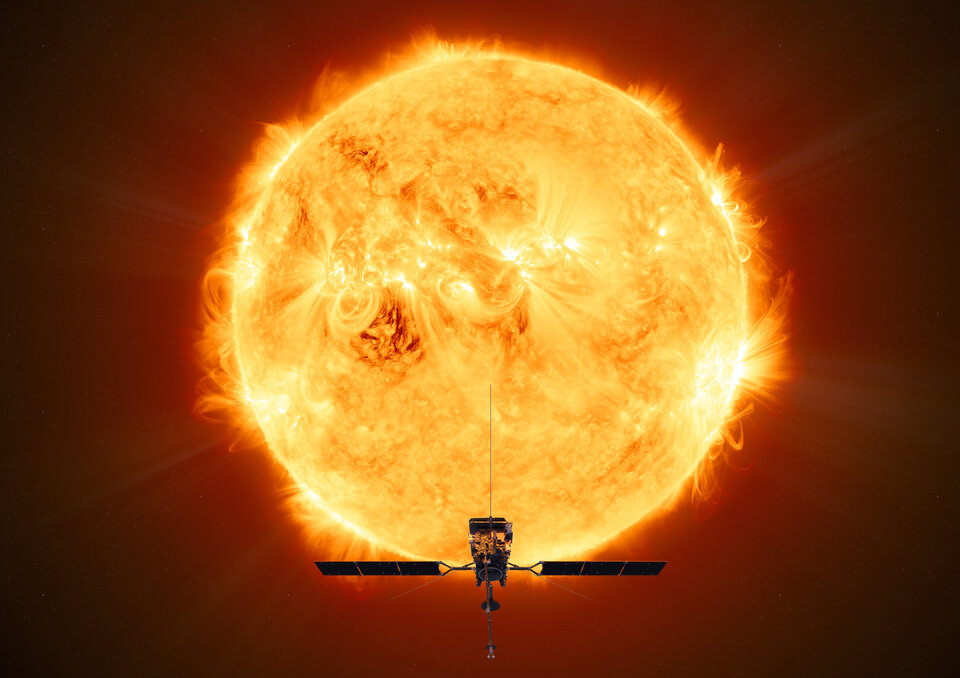
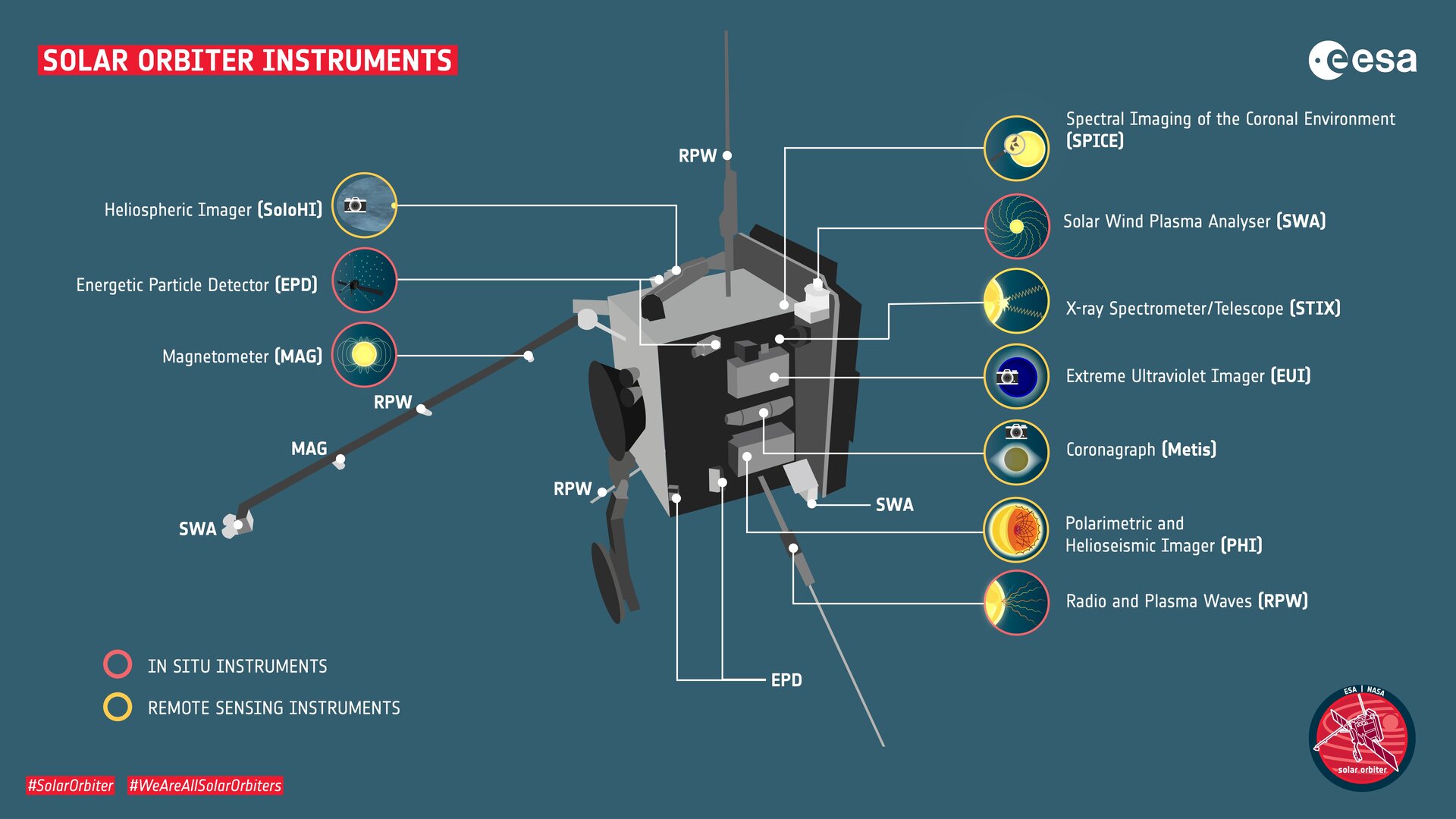
The Solar Orbiter (SolO) is a joint project by the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA to study the behavior of the Sun with the aim of discovering how it creates and controls the heliosphere. The SolO satellite was launched on the 10th February 2020 and is set to achieve its intended elliptical orbit around the Sun, with a perihelion of approximately 900 million miles, by 2022. This will leave the satellite orbiting closer to the Sun than Mercury.
The heliosphere is the giant bubble of plasma that surrounds the entire solar system and influences the astronomical bodies within it, including Earth. To understand the Sun’s behavior, SolO will obtain measurements of solar energetic particles (SEPs), which consist of protons, electrons and HZE ions with energies ranging from 10keV to many GeVs. The best-known manifestation of SEPs on Earth is the Aurora Borealis (northern lights), which occurs when SEPs interact with gases in our atmosphere. SEPs are important as they affect hardware in space, weather and life in space, and impact the environment here on Earth. By obtaining measurements of SEPs closer to the Sun, where they have experienced minimal effects from travelling through space, SolO will allow scientists to gain greater and more credible insight into the behavior of these particles.
To understand the creation and control of the heliosphere, SolO aims to provide answers to the following questions:
- How does solar wind plasma originate in the Sun’s corona?
- How does the solar dynamo (the process that generates the Sun’s magnetic field) work?
- How do solar eruptions produce energetic particle radiation that fills the heliosphere?
To address the latter, the solar orbiter has an energy particle detector (EPD), an instrument suite comprising 5 telescopic sensors that will measure the composition, timing, energy levels, and presence of different SEPs. Rapita Systems are proud to have had a role in the verification of the EPD.
The EPD has 5 sensors to detect particles, which operate at overlapping energy levels:
- Suprathermal electrons ions and neutrals telescope (STEIN) – uses silicon semiconductor detectors to measure particles in the energy range ~3-100keV.
- Electron Proton telescope (EPT) – uses 2 telescopes to measure electrons in 20keV-700keV range and protons in the 20keV-9MeV range.
- Low Energy telescope (LET) – measures species in the range 1.5-60 MeV.
- High Energy Telescope (HET) – measures high energy particle ranging up to 200 MeV. This sensor provides information for the largest SEP events, which can produce high energy, damaging interplanetary radiation levels.
- Suprathermal ion spectrograph (SIS) – measures the composition of heavy ions in the range of 8keV/n-10MeV.
The sensors use different techniques for particle detection and separation: time-of-flight mass spectrometry, electrostatic deflection and the magnet/foil technique. Like most particle detectors, these sensors will be able to establish properties such as spin, charge and distribution functions of the particles they detect.
The sensors on the EPD are linked to an instrument control unit (ICU), which is the single point of connection between the spacecraft and the EPD. The ICU provides the data and power interface for the interactions between the spacecraft and the EPD and allows information to be shared between the sensors to facilitate synchronized operations.
The ICU was designed to manage the sensors’ control and monitoring, timing clock, data collection & compression and telemetry. The ICU, which is the brain of the EPD was developed by the University of Alcala in Spain who used the Rapita Verification Suite (RVS) to perform analysis on the system. RVS is a software verification tool suite optimized for DO-178 projects - find out how it was used in development of the ICU’s software. Get the latest updates of the solar orbiter mission on the ESA website.

 Rapita System Announces New Distribution Partnership with COONTEC
Rapita System Announces New Distribution Partnership with COONTEC
 Rapita partners with Asterios Technologies to deliver solutions in multicore certification
Rapita partners with Asterios Technologies to deliver solutions in multicore certification
 SAIF Autonomy to use RVS to verify their groundbreaking AI platform
SAIF Autonomy to use RVS to verify their groundbreaking AI platform
 RVS gets a new timing analysis engine
RVS gets a new timing analysis engine
 How to measure stack usage through stack painting with RapiTest
How to measure stack usage through stack painting with RapiTest
 What does AMACC Rev B mean for multicore certification?
What does AMACC Rev B mean for multicore certification?
 How emulation can reduce avionics verification costs: Sim68020
How emulation can reduce avionics verification costs: Sim68020
 How to achieve multicore DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
How to achieve multicore DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
 How to achieve DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
How to achieve DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
 Certifying Unmanned Aircraft Systems
Certifying Unmanned Aircraft Systems
 DO-278A Guidance: Introduction to RTCA DO-278 approval
DO-278A Guidance: Introduction to RTCA DO-278 approval
 NXP's MultiCore for Avionics (MCFA) Conference
NXP's MultiCore for Avionics (MCFA) Conference
 DO-178C Multicore In-person Training (Heathrow)
DO-178C Multicore In-person Training (Heathrow)
 Avionics and Testing Innovations
Avionics and Testing Innovations
 Certification Together International Conference (CTIC)
Certification Together International Conference (CTIC)