The efficiency of our tools is an important way in which we can offer our customers savings in terms of time and money. We are constantly refining our tools to improve this efficiency, which has recently included the adoption of new Ada language processing technology. The incorporation of libadalang will allow quicker support of new language features and speed up the analysis of customer code, especially for larger projects.
Background: Parsing in RVS
Rapita Verification Suite (RVS) contains a range of products to help customers analyze and test critical software, providing tools for instrumentation of timing and coverage, tracing, test generation and static analysis. These tools share a preparation database that contains an abstract representation of all the source code for a given customer project. Currently Rapita supports Ada, C, C++ and several assembly languages. A language-specific parser reads a source file and puts a representation of the code in the database. The structure is shown below.
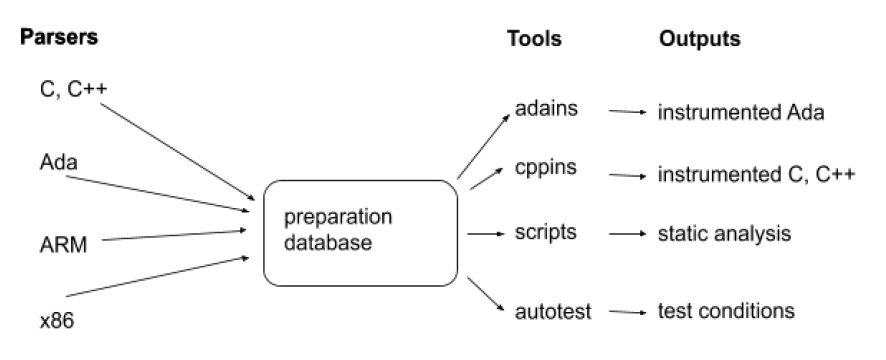
Once the project is in the database, separate analysis tools can be run as needed, including interactive ones that allow you to guide the activity. This structure allows parsers and tools to be added or extended without disrupting anything else. In the rest of this article, we consider the process of safely changing an existing parser. We shall describe how and why Rapita changed the parser for C and C++, without disrupting customers’ work, and how it will do the same for Ada.
The evolution of programming languages
C and C++ support was originally provided by separate ad-hoc parsers. Programming languages are periodically revised, introducing new language rules and constructions, which customers wish to use (often to support third-party libraries). The ad-hoc parsers became hard to extend and maintain to track those changes. Two years ago, Rapita developed a replacement parser based on a production C and C++ compiler that would support those languages as they stood, and as they continued to evolve.
That new support for C and C++ was introduced carefully. First, it had to pass the same extensive suite of end-to-end tests as the existing parsers. Next, the old and new components were provided side-by-side, with the old ones used by default. The new one could, however, be selected explicitly, allowing its use for new integrations, but with a fallback available to the old components if necessary. Eventually, existing integrations also used the new component, and the old was deprecated. Finally, the old one was discarded. The Rapita tools continued to take their input from the database and could remain unchanged.
In a similar way to C and C++, Ada too has evolved: Ada 83, 95, 2005, 2012 and soon 2020. Unlike the ad-hoc parsers originally used for C and C++, Rapita’s Ada processing uses the GNAT Ada compiler, which does track language changes. As part of the process, however, GNAT produces an elaborate intermediate form (ASIS) that has begun to creak with age. A separate Rapita program converts ASIS into database entries. Adding support for more language features has not always been straightforward, and the two-stage process is relatively slow and inefficient since the extra intermediate form must be written out by GNAT and read back in by the conversion program.
Harnessing the power of libadalang

AdaCore, GNAT’s author, has developed a new library libadalang specifically written to make it easier to build tools to work with Ada programs, for example better IDEs. Rapita is using libadalang to build a replacement for the GNAT-based Ada processing in the pipeline shown above. From a customer’s perspective, this will allow quicker support of new language features. Avoiding significant IO between two separate programs reduces the clock time taken to produce the preparation database, speeding up the analysis of customer code, especially for larger projects. Finally, the process for introducing the new component will mimic the one described above, successfully used for C and C++, to ensure a smooth transition.

 RVS 3.24 accelerates multicore software verification
RVS 3.24 accelerates multicore software verification
 Rapita Systems and Avionyx Announce Strategic Partnership to Offer Best-in-class Avionics Solutions
Rapita Systems and Avionyx Announce Strategic Partnership to Offer Best-in-class Avionics Solutions
 Rapita System Announces New Distribution Partnership with COONTEC
Rapita System Announces New Distribution Partnership with COONTEC
 RVS gets a new timing analysis engine
RVS gets a new timing analysis engine
 How to measure stack usage through stack painting with RapiTest
How to measure stack usage through stack painting with RapiTest
 What does AMACC Rev B mean for multicore certification?
What does AMACC Rev B mean for multicore certification?
 How emulation can reduce avionics verification costs: Sim68020
How emulation can reduce avionics verification costs: Sim68020
 How to achieve multicore DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
How to achieve multicore DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
 How to achieve DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
How to achieve DO-178C certification with Rapita Systems
 Certifying Unmanned Aircraft Systems
Certifying Unmanned Aircraft Systems
 DO-278A Guidance: Introduction to RTCA DO-278 approval
DO-278A Guidance: Introduction to RTCA DO-278 approval
 Embedded World 2026
Embedded World 2026
 Test what you fly - Real code, Real Conditions Webinar
Test what you fly - Real code, Real Conditions Webinar
 Avionics Certification Q&A: CERT TALK
Avionics Certification Q&A: CERT TALK